BIOS/UEFI problems can lead to various boot, performance, and configuration issues for a computer. Here are some common BIOS/UEFI problems and how to address them:
1. Boot Device Not Found/Error
- Cause: The BIOS/UEFI might not detect the boot device due to incorrect boot settings, a disconnected cable, or a corrupted boot drive.
- Solution:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI settings and ensure the correct boot drive is set as the primary boot device.
- Verify that the SATA or NVMe drive is properly connected.
- Repair the boot sector using a Windows installation disk.
2. System Date and Time Reset
- Cause: The CMOS battery is dead, leading to BIOS settings resetting every time the computer is turned off.
- Solution: Replace the CMOS battery (typically a CR2032 coin-cell battery).
3. Overclocking Failure
- Cause: Overclocking settings for CPU or RAM may be unstable, leading to boot failures or system crashes.
- Solution:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI and reset to default settings.
- Gradually adjust the overclock settings to find a stable configuration, or disable overclocking entirely.
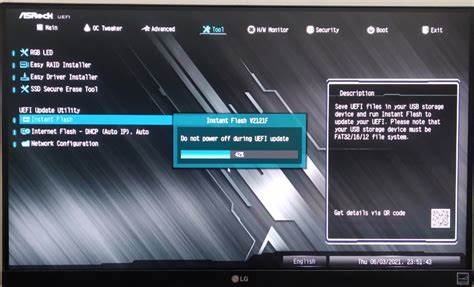
4. BIOS/UEFI Update Issues
- Cause: Updating BIOS/UEFI firmware can sometimes fail due to power loss, compatibility issues, or interruptions during the process.
- Solution:
- Try to reflash the BIOS/UEFI using a USB stick and the correct firmware version.
- Some motherboards have a BIOS recovery feature that allows you to recover from a failed update. Refer to your motherboard manual.
5. No Display on Boot
- Cause: Incorrect BIOS settings, hardware issues, or an incompatible graphics card can prevent the system from displaying output.
- Solution:
- Reset BIOS/UEFI to default settings by clearing the CMOS.
- Ensure the monitor cable is properly connected, and test the system with a different graphics card if possible.
6. Unable to Enter BIOS/UEFI Setup
- Cause: The wrong key is being pressed during startup, or a fast boot setting is enabled that skips BIOS access.
- Solution:
- Typically, pressing DEL, F2, F10, or ESC during startup will allow you to enter BIOS/UEFI.
- If Fast Boot is enabled, try holding the BIOS key while pressing the power button, or use Windows advanced restart options to boot into UEFI firmware.
7. BIOS/UEFI Not Detecting Hardware
- Cause: The motherboard may have compatibility issues, or the hardware may not be properly connected.
- Solution:
- Reseat the hardware, like the RAM, CPU, or storage device.
- Check the compatibility list of your motherboard to ensure the hardware is supported.
- Update the BIOS/UEFI firmware to improve compatibility with newer hardware.
8. System Keeps Restarting
- Cause: Corrupted BIOS settings, incompatible hardware, or improper power delivery can cause a restart loop.
- Solution:
- Reset BIOS/UEFI to default settings.
- Check all power connections and ensure the power supply is sufficient.
- Test the system with minimal components to isolate the cause.
9. Keyboard/Mouse Not Working in BIOS/UEFI
- Cause: BIOS/UEFI may not recognize USB devices due to incorrect settings or hardware incompatibility.
- Solution:
- Plug the keyboard or mouse into a USB 2.0 port instead of USB 3.0.
- Enable USB Legacy Support in the BIOS/UEFI settings if you can access it.
10. Slow BIOS/UEFI Boot Time
- Cause: BIOS settings such as Full Memory Initialization or an extensive hardware POST can lead to slower boot times.
- Solution:
- Enable Fast Boot or Quick Boot in the BIOS settings to skip some of the initial tests.
- Disable hardware checks that are not needed (e.g., full memory tests).
11. Corrupted BIOS Settings
- Cause: Settings can become corrupted due to power loss, failed updates, or incorrect manual changes.
- Solution:
- Reset BIOS/UEFI settings to default by clearing the CMOS.
- Update the BIOS/UEFI to the latest version to resolve any potential bugs.
12. CPU Fan or System Fan Errors
- Cause: BIOS may not detect the CPU fan or other system fans if they are incorrectly connected, leading to warnings or system shutdowns.
- Solution:
- Ensure that all fans are connected to the correct headers.
- Check BIOS settings for fan control and make sure the CPU Fan Header is used for the CPU fan.
13. BIOS Password Issues
- Cause: If a password is set and forgotten, access to the BIOS/UEFI is restricted.
- Solution:
- Clear CMOS by removing the CMOS battery or using the CMOS jumper on the motherboard.
- Contact the motherboard manufacturer for assistance if there is a supervisor password that cannot be cleared.
14. Compatibility Problems with New Hardware
- Cause: Older BIOS/UEFI versions may not recognize newer hardware components like CPUs, RAM, or graphics cards.
- Solution:
- Update the BIOS/UEFI firmware to the latest version to add support for new hardware.
- Verify compatibility between your motherboard and the hardware you want to install.
If you encounter any of these BIOS/UEFI problems, taking a systematic approach to troubleshooting and referring to your motherboard’s manual can often help resolve the issue.