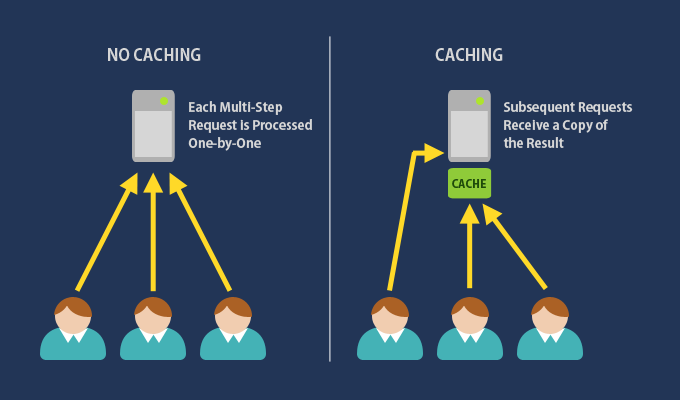
Pros of Virtual Machines:
- Efficient Resource Utilization:
- Multiple virtual machines can run on a single physical server, optimizing the use of CPU, memory, and storage resources.
- Cost Savings:
- Virtualization reduces the need for physical hardware, which leads to lower costs for equipment, maintenance, and space requirements.
- Scalability:
- Virtual machines can be easily created, modified, or deleted to adjust to workload demands, making them ideal for dynamic environments.
- Isolation and Security:
- VMs run in isolated environments, which helps prevent issues in one VM from impacting others. This isolation enhances security and stability, especially for testing.
- Ease of Backup and Recovery:
- Since VMs are just files, they can be easily backed up, cloned, or restored, providing excellent disaster recovery capabilities.
- Portability:
- VMs can be moved between different host machines with minimal downtime, allowing for better load balancing and hardware maintenance.
- Testing and Development:
- Developers use VMs to test applications in different environments without the need for dedicated physical hardware, allowing for efficient software testing and experimentation.
Cons of Virtual Machines:
- Performance Overhead:
- VMs consume resources to run the virtualization software, resulting in overhead that can make them slower compared to running directly on physical hardware.
- Resource Contention:
- Multiple VMs running on the same physical machine can lead to resource contention, where each VM competes for CPU, memory, and I/O, potentially affecting performance.
- Licensing Costs:
- Licensing virtual machine software and the guest operating systems can add significant costs, especially if running multiple VMs.
- Complex Management:
- Managing a large number of VMs can become complex and may require specialized tools and expertise, especially in terms of updates, resource allocation, and monitoring.
- Security Risks:
- Although VMs provide isolation, vulnerabilities in the virtualization software (hypervisor) could be exploited, potentially allowing malicious code to access the host system or other VMs.
- Hardware Dependency:
- The performance of VMs is limited by the underlying physical hardware. Insufficient resources in the host can lead to poor performance or crashes for all the VMs running on it.
- Storage Overhead:
- Each VM requires its own operating system, applications, and storage space. When many VMs are used, this can lead to significant storage requirements.
Virtual machines are versatile and powerful tools, particularly for environments that require flexibility, but they come with performance trade-offs and management challenges. Choosing between VMs and physical hardware depends on specific needs like performance, scalability, and cost considerations.