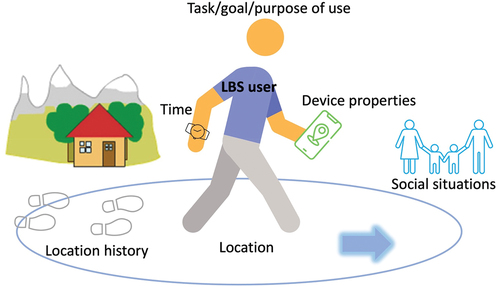
Location-Based Web Services (LBWS) use geolocation data to provide personalized and relevant content or services based on a user’s current location. They offer various benefits across many industries, improving user experience, engagement, and operational efficiency. Here are the key benefits of location-based web services:
1. Personalized User Experience
- Relevant Content: LBWS can provide tailored content, like news, events, or offers based on where users are located. For instance, a weather app can automatically show the weather in a user’s current city without manual input.
- Localized Search: Location-based services make it easy to find nearby places, like restaurants, gas stations, or businesses. Search results are filtered to be more relevant, saving users time and effort.
2. Improved Marketing and Customer Engagement
- Location-Based Advertising: Businesses can send promotions, discounts, and notifications to users near their stores, increasing the chance of foot traffic and sales. For example, retailers can use geofencing to send targeted offers when users enter a specific area.
- Increased Engagement: LBWS enhances customer engagement by providing personalized recommendations and information. Users are more likely to interact with content and services that are contextually relevant to their current location.
3. Enhanced Convenience and Utility
- Efficient Navigation: Apps like Google Maps, Apple Maps, and Waze provide real-time directions, helping users navigate to their destinations efficiently, which improves user convenience and minimizes travel time.
- On-Demand Services: LBWS are fundamental for services like ride-hailing (Uber, Lyft), food delivery (DoorDash, Uber Eats), and home services (TaskRabbit). They help match users with nearby drivers or service providers, improving response times and convenience.
4. Better Resource Management and Efficiency
- Fleet and Workforce Management: Companies can use LBWS to monitor the real-time locations of their assets, vehicles, or employees. This helps optimize routes, reduce fuel costs, and ensure workers are in the right places for maximum efficiency.
- Geofencing for Automation: Organizations can automate specific actions using geofencing, such as logging workers’ attendance when they enter or leave a job site. It also enables location-specific notifications, like informing warehouse staff when deliveries are near.
5. Improved Safety and Security
- Emergency Services: LBWS play a critical role in enhancing safety. Emergency response systems use location data to provide immediate help based on the caller’s location, helping emergency services (ambulances, police) arrive quickly.
- Location Sharing: Users can share their current location with family or friends for safety purposes. Applications like Google Maps provide a “share location” feature that allows users to ensure loved ones know where they are in real time.
6. Real-Time Updates and Tracking
- Traffic and Transit Information: Users benefit from real-time traffic information, which helps them avoid congestion and choose the best route. Public transportation apps also use location data to provide accurate information on transit schedules, delays, and estimated arrival times.
- Delivery and Order Tracking: Location-based services allow customers to track deliveries in real time. This transparency helps manage customer expectations, reducing uncertainty and improving satisfaction.
7. Enhanced Social Connectivity
- Check-Ins and Social Media Sharing: Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram enable users to “check in” at their current location, share experiences, and recommend places to friends. This adds a social element to users’ activities, helping them connect with others.
- Location-Based Friend Suggestions: Apps like Snapchat and dating services like Tinder can use location data to suggest people who are nearby, enhancing social connectivity and relevance.
8. Better Business Insights and Decision-Making
- Customer Behavior Analysis: Location data helps businesses understand customer movement patterns, foot traffic, and preferences. For instance, retailers can analyze which areas get the most visitors and optimize their layout or marketing strategies accordingly.
- Market Research: Companies can use location-based data to analyze consumer behavior geographically, helping them make informed decisions on where to open new stores or launch marketing campaigns.
9. Efficient Location-Specific Services
- Local Assistance: LBWS make it easier to find local services like hospitals, police stations, pharmacies, etc. Location-based searches provide users with essential services nearby, especially useful in unfamiliar locations.
- Dynamic Pricing: Services like ride-sharing apps use location data to adjust pricing based on demand in specific areas (surge pricing). This allows better matching of supply and demand, improving efficiency for service providers.
10. Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences
- AR Gaming: Games like Pokémon GO use location-based services to create immersive experiences where players interact with virtual objects in the real world. This is possible due to GPS and geolocation data integration.
- Interactive City Tours: AR apps provide users with enhanced experiences by overlaying information on their device’s screen, such as historical facts about buildings or landmarks during a city tour.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Privacy Concerns:
- LBWS require access to users’ location data, which raises privacy concerns. Users need to be informed about data collection practices, and explicit consent must be obtained. Developers must comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA to ensure data privacy.
- Battery Consumption:
- Continuous tracking of location using GPS can drain the battery, which impacts user experience. Developers need to optimize how and when location data is collected to minimize this impact.
- Accuracy Issues:
- The accuracy of location data can vary depending on the technology used (e.g., GPS, Wi-Fi). Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect services, such as providing irrelevant offers or incorrect navigation, reducing user trust.
- Connectivity Requirements:
- LBWS often require a stable internet connection to provide real-time services. In areas with poor connectivity, such services may fail to deliver an optimal experience.
Despite these challenges, location-based web services significantly enhance user experience, engagement, and operational efficiency by providing context-aware and personalized interactions. Balancing privacy, accuracy, and usability is key to maximizing the benefits while mitigating the potential downsides.