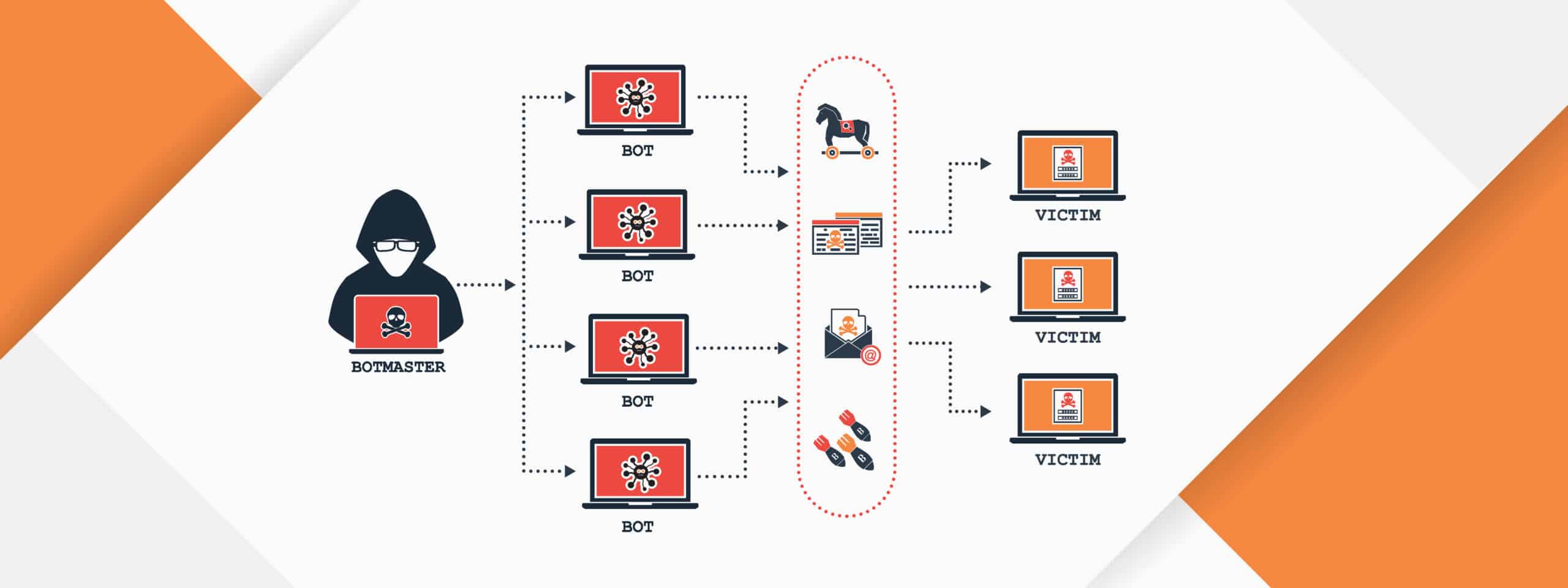
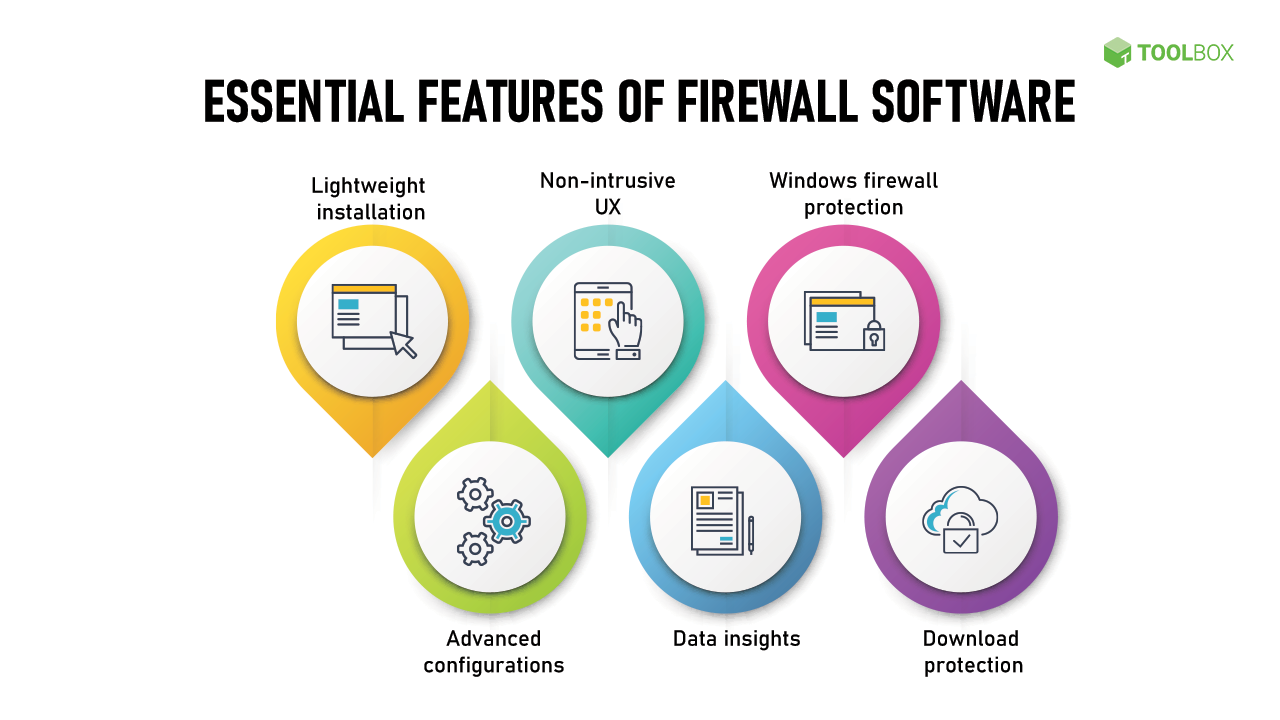
Keyloggers are a type of surveillance software or hardware designed to record keystrokes made on a computer or mobile device. They can be used for various purposes, including legitimate monitoring, but they are often associated with malicious intent. Here’s what you need to know about keyloggers:
Types of Keyloggers
- Software Keyloggers:
- Installed Programs: These are software applications installed on a device to log keystrokes and capture user activity. They can be hidden from the user, making detection difficult.
- Browser-based Keyloggers: Some keyloggers operate within web browsers and can record input fields on web pages.
- Hardware Keyloggers:
- Physical Devices: These are small devices connected between the keyboard and the computer, recording keystrokes as they are typed. They can be difficult to detect as they do not rely on software.
- Wireless Keyloggers: These devices intercept wireless signals from wireless keyboards, capturing keystrokes without a physical connection.
How Keyloggers Work
- Recording Keystrokes: Keyloggers monitor keyboard inputs and store them in a log file, which can later be retrieved by the person who installed the keylogger.
- Capturing Screenshots: Some advanced keyloggers can capture screenshots at regular intervals or record video of user activity.
- Network Monitoring: Keyloggers can also monitor network traffic to capture sensitive information sent over the internet, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
Common Uses of Keyloggers
- Legitimate Monitoring:
- Parental Control: Parents may use keyloggers to monitor their children’s online activity and ensure their safety.
- Employee Monitoring: Employers might use keyloggers to track employee activity on company devices to ensure productivity and prevent data leaks.
- Malicious Intent:
- Identity Theft: Cybercriminals use keyloggers to steal sensitive information, such as passwords, banking details, and personal data, leading to identity theft.
- Espionage: Keyloggers can be used by attackers to gather sensitive information from competitors or individuals for corporate espionage.
Risks and Dangers
- Privacy Violations: Keyloggers can invade personal privacy by recording sensitive information without the user’s consent or knowledge.
- Data Theft: The information captured by keyloggers can be used for malicious activities, such as fraud, identity theft, and unauthorized access to accounts.
- Unauthorized Surveillance: Keyloggers can be used to monitor individuals without their awareness, leading to significant breaches of trust and legality.
Detection and Prevention
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software:
- Use Security Software: Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software that can detect and remove keyloggers and other malicious programs.
- Regular Scans: Schedule regular scans of your device to identify and eliminate potential threats.
- Keep Software Updated:
- Update OS and Applications: Regularly update your operating system and applications to protect against vulnerabilities that keyloggers may exploit.
- Use a Firewall:
- Network Protection: A firewall can help block unauthorized access and prevent keyloggers from communicating with external servers.
- Educate Users:
- Awareness and Training: Educate users about the risks of keyloggers and encourage safe browsing practices, such as avoiding suspicious downloads and clicking on unknown links.
- Password Managers:
- Secure Passwords: Use password managers to securely store and fill in passwords, reducing the risk of exposing sensitive information through keystrokes.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Add an Extra Layer of Security: Implement 2FA on accounts whenever possible, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access even if they capture your password.
Legal Considerations
- Legality: The use of keyloggers for monitoring is subject to legal restrictions that vary by jurisdiction. In many places, using a keylogger without consent is illegal.
- Compliance: Organizations must comply with data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, when using monitoring tools.
Conclusion
Keyloggers pose significant risks to privacy and security, making it essential for individuals and organizations to be aware of their presence and potential consequences. By taking proactive measures such as using security software, keeping systems updated, and educating users, you can minimize the risk of falling victim to keyloggers and protect sensitive information.