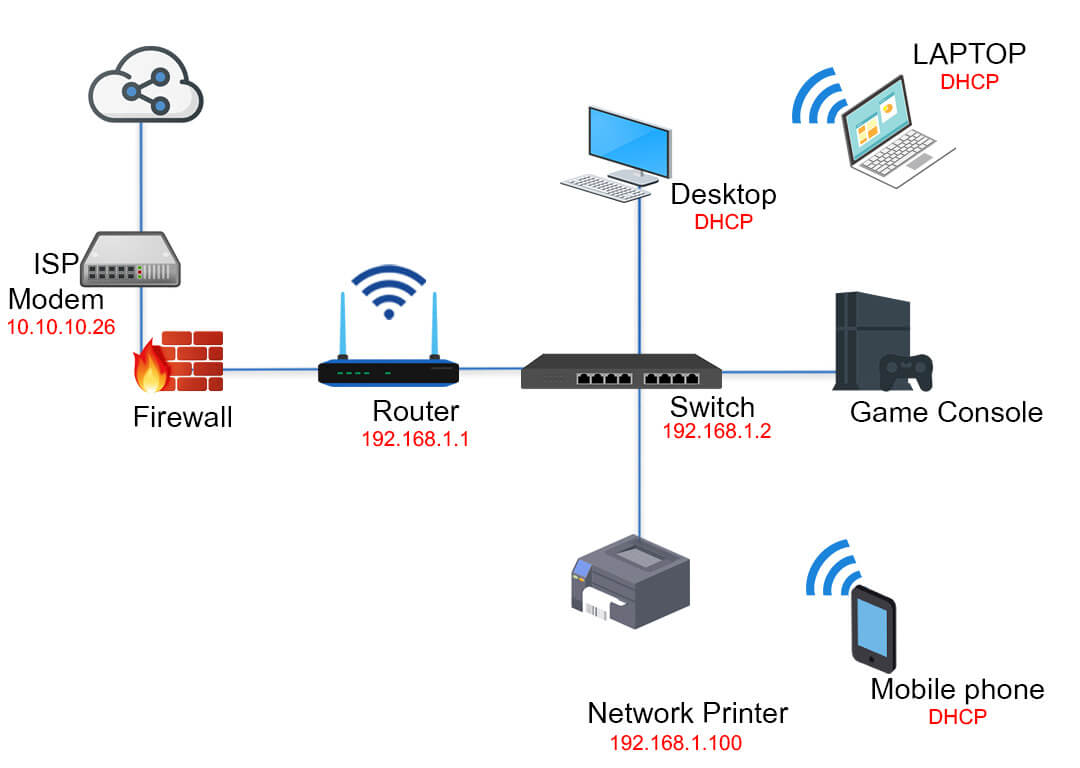
Setting up a home network involves several factors to ensure it’s reliable, secure, and optimized for your needs. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when setting up your home network:
1. Internet Connection Type
- Broadband Connection: Most homes use a broadband connection (cable, fiber-optic, DSL, or satellite) for internet access. Ensure your internet plan meets your speed requirements for all devices—especially for streaming, gaming, or heavy-duty work.
- Cable or Fiber-Optic: These types of connections offer higher speeds, lower latency, and better reliability compared to DSL or satellite internet.
- Satellite: For rural or remote areas without broadband, satellite internet is an option, but it often has higher latency and variable performance.
- Mobile Hotspots: Consider this option if traditional broadband connections aren’t available.
2. Router Selection
- Choose the Right Router: The router you select determines the performance of your home network. A dual-band or tri-band router can offer a good balance between speed, coverage, and stability.
- Dual-Band Router: Operates on two frequencies—2.4 GHz (good for long-range and older devices) and 5 GHz (faster for modern devices within close range).
- Tri-Band Router: Offers an additional 5 GHz band for even better performance and more simultaneous connections.
- Consider Wi-Fi Standard: Make sure your router supports the latest Wi-Fi standards (Wi-Fi 6 or 802.11ax) for faster, more efficient, and stable internet connections compared to older versions (Wi-Fi 5 or 802.11ac).
- Mesh Network Systems: For larger homes or areas with poor Wi-Fi coverage, a mesh network system may be more suitable. Mesh systems use multiple access points to cover a larger area with a consistent Wi-Fi signal.
3. Network Security
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: The latest Wi-Fi encryption protocol, WPA3, provides stronger security compared to older WPA2, reducing risks from cyberattacks or unauthorized access.
- Use a Strong Wi-Fi Password: A complex, unique password helps protect your network from unwanted access.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): This feature is easy to exploit, so it’s best to turn it off.
- Firewall Settings: Ensure your router has a built-in firewall enabled to block unwanted traffic.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your router firmware up-to-date to ensure the latest security features and improvements are applied.
- Network Segmentation: Create separate networks for different types of devices—IoT devices, guests, and sensitive systems—using different SSIDs or VLANs.
4. Wired vs. Wireless Network
- Use Ethernet for High-Performance Devices: For desktops, servers, game consoles, or devices where a fast, reliable connection is essential, Ethernet provides better speeds and stability compared to Wi-Fi.
- Wireless for Mobility: For laptops, tablets, smartphones, and IoT devices where mobility and convenience are important, Wi-Fi is the preferred option.
- Mix of Both: In many homes, a combination of Ethernet and Wi-Fi is used to balance performance with flexibility.
5. Placement of Network Equipment
- Router Location: Place the router in a central location of your home to maximize Wi-Fi coverage. A high location (like a second-story corner) can also help improve signal quality.
- Avoid Obstacles: Position your router away from walls, appliances, and other electronic devices to minimize signal interference.
- Mesh Network Placement: For homes with poor Wi-Fi coverage, consider strategically placing additional mesh nodes in areas where signals need boosting.
- Consider Smart Plugs or Powerline Adapters: If you need additional wired connections but can’t run cables easily, smart plugs or powerline adapters can help.
6. Wired and Wireless Devices
- Count Devices: Evaluate how many wired and wireless devices you’ll connect to the network—smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, smart speakers, printers, and so on. This will help determine if a single-band or dual-band router is enough or if you need a mesh system.
- Prioritize Devices: For devices requiring higher bandwidth (like gaming consoles, streaming devices), giving them priority in the network settings can help ensure they get the necessary resources.
- IoT Devices: Ensure your network supports all the smart home devices you plan to use—like smart thermostats, security cameras, smart bulbs, etc.
7. Backup and Storage
- Data Backup: Backup solutions like external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS) devices, or cloud services are essential to protect important data from loss due to hardware failure, accidental deletion, or cyber-attacks.
- Consider RAID Configuration: Setting up a RAID array in your NAS can provide extra redundancy and data protection.
- Cloud Backup: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive offer an affordable and convenient way to back up data remotely.
8. Quality of Service (QoS) Settings
- QoS allows you to prioritize network traffic for specific applications or devices. For example, gaming, video streaming, or video conferencing should have higher priority to minimize latency and buffering.
- Adjust the QoS settings on your router to make sure critical applications get enough bandwidth.
9. Network Access Control
- Parental Controls: Configure parental controls on your router to block or restrict access to inappropriate content or limit online activity for children.
- Guest Network: Set up a separate Wi-Fi network for guests to provide internet access without allowing access to your main devices and files.
- Device Access Control: Limit access to sensitive devices or services based on IP address, MAC address, or other criteria.
10. Testing and Optimization
- Run a Speed Test: After setting up your network, run a speed test to check for speed and stability. This will help you identify areas where improvements are needed (like moving the router or using a mesh system).
- Network Scanner: Use a network scanner to detect devices connected to your network and check for any unauthorized access.
- Optimize Wireless Channels: In a crowded area with many networks, change the Wi-Fi channel of your router to minimize interference and improve performance.
- Update Firmware: Make sure the firmware of your router is up-to-date for the latest security patches and features.
These factors will help you set up a home network that is fast, reliable, secure, and well-suited to your needs.




