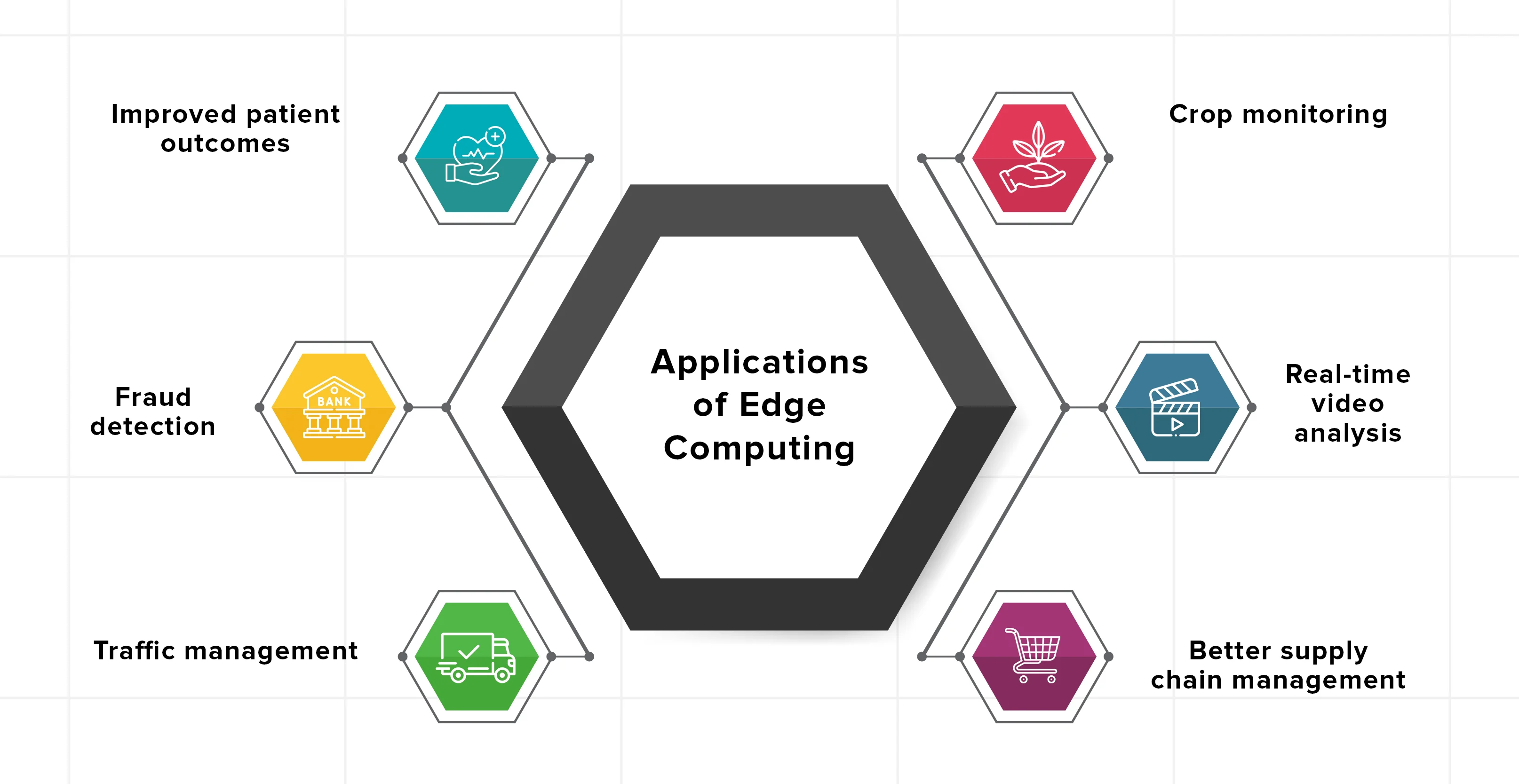
Edge Computing is gaining traction due to its ability to process data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and improving efficiency. Here are some common use cases for edge computing across industries:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
Use Case: Real-Time Data Processing
- Examples:
- Smart home devices like thermostats and security cameras process data locally for faster response times.
- Industrial IoT devices in factories monitor machinery and predict maintenance needs without relying on cloud connectivity.
- Benefit: Minimizes latency and ensures uninterrupted operation even if the network is unreliable.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Use Case: Onboard Decision-Making
- Examples:
- Self-driving cars use edge computing to analyze sensor data (cameras, LIDAR, radar) in real time for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Fleet management systems process location and condition data locally to improve efficiency.
- Benefit: Immediate responses critical for safety and efficiency.
3. Healthcare
Use Case: Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Examples:
- Wearable devices (e.g., heart monitors) analyze health data locally to alert users or doctors to potential issues.
- Operating rooms use edge computing for real-time analysis of patient vitals during surgeries.
- Benefit: Faster insights and reduced dependence on high-speed internet, especially in remote areas.
4. Retail
Use Case: Enhanced Customer Experiences
- Examples:
- In-store analytics systems process customer movement data to optimize store layouts.
- Smart shelves detect inventory levels and send alerts or reorder products locally.
- Benefit: Immediate insights improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
5. Smart Cities
Use Case: Real-Time Monitoring and Automation
- Examples:
- Traffic management systems use edge devices to monitor and control traffic lights based on congestion.
- Public safety cameras analyze footage locally for threats, minimizing bandwidth use.
- Benefit: Enables responsive and scalable urban infrastructure.
6. Content Delivery and Gaming
Use Case: Low-Latency Services
- Examples:
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) store popular media closer to users for faster streaming.
- Cloud gaming platforms reduce lag by processing inputs and rendering frames at edge nodes.
- Benefit: Improves user experience for latency-sensitive applications.
7. Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Use Case: Predictive Maintenance and Automation
- Examples:
- Edge devices analyze machine performance data to predict failures and optimize production lines.
- Robots and automated systems perform real-time adjustments to improve manufacturing precision.
- Benefit: Enhances productivity and reduces downtime.
8. Energy and Utilities
Use Case: Smart Grids and Remote Monitoring
- Examples:
- Smart meters monitor energy usage locally and optimize grid distribution.
- Edge devices in wind farms analyze turbine performance and environmental conditions.
- Benefit: Enables efficient energy management and reduces costs.
9. Telecommunications
Use Case: Network Optimization
- Examples:
- 5G base stations use edge computing to process data locally, reducing backhaul to centralized servers.
- Mobile apps optimize content delivery using nearby edge servers.
- Benefit: Enhances service quality and reduces network congestion.
10. AR/VR Applications
Use Case: Real-Time Interaction
- Examples:
- Augmented reality in retail or healthcare (e.g., AR-assisted surgeries) relies on edge computing for immediate data processing.
- Virtual reality gaming benefits from reduced latency for smoother experiences.
- Benefit: Makes interactive experiences seamless and responsive.
11. Agriculture
Use Case: Precision Farming
- Examples:
- Drones with edge devices analyze soil health and crop conditions during flights.
- Automated irrigation systems adjust water delivery based on local weather and soil data.
- Benefit: Improves yields while conserving resources.
12. Financial Services
Use Case: Fraud Detection and Compliance
- Examples:
- ATMs and point-of-sale (POS) systems detect fraud patterns locally for instant alerts.
- Trading platforms use edge devices to analyze market data for ultra-low-latency decisions.
- Benefit: Enhances security and speeds up transaction processing.
Benefits of Edge Computing in These Use Cases
- Reduced Latency: Immediate data processing leads to faster responses.
- Lower Bandwidth Use: Only critical data is sent to central servers, reducing costs.
- Enhanced Reliability: Systems can function even with limited or no internet connectivity.
- Improved Privacy: Sensitive data can be processed locally, reducing the risk of breaches.




